Vendor Name: PMI
Exam code: PMI-SP
Exam Name: PMI Scheduling Professional
Click the link below to get full version
http://www.certifyguide.com/exam/PMI-SP/
|
Question: 1
|
Once the project's WBS has
been created what process may happen next?
A. Estimate activity resources
B. Define activities
C. Estimate activity durations
D. Sequence activities
|
Answer: B
|
Explanation:
The define activities process
is the process that may begin once the project's WBS has been completed and approved. It is possible, in
some projects, to complete the WBS and
the activity list at the same time.
Answer option D is incorrect. Sequencing the activities cannot happen until the
activity list has been created. Answer option A is incorrect. Estimating
activity resources is dependent on the activity list, so this choice is not valid. Answer option C is incorrect. Estimate
activity durations are dependent on the activity list, so this choice is not valid.
|
Question: 2
|
Which of the following
scheduling techniques identifies the successor activities and the predecessor activities
to assist the project manager in sequencing the project work?
A. Precedence Diagramming
Method
B. Schedule network template
C. Dependency determination
D. Activity on the Node
|
Answer: A
|
Explanation:
The Precedence Diagramming
Method uses both predecessors and successors as nodes in the project network diagram. The PDM approach is the most common network diagram approach used.
Answer option C is incorrect. Dependency
determination identifies the order of the project work. Answer option B is incorrect. The schedule
network template is a tool that uses a previous project network diagram as a base for the current project network diagram. Answer option D is incorrect. Activity on the node
laces activities on circles within a
network diagram. It is an example of the
precedence diagramming method.
|
Question: 3
|
You are the project manager of
the NHGQ project for your company. You must create and distribute performance reports every week to your key
project stakeholders. What communication technique do you normally use to distribute reports?
A. Push technique
B. Many-to-many
C. One-to-one
D. Pull technique
|
Answer: A
|
Explanation:
Performance reports are
distributed through the push technique. This means that the project manager distributes the reports regularly through a mechanism, such as email. Answer option C is incorrect. One-to-one
technique describes a conversation between two people. Answer option B is incorrect. Many-to-many
technique describes a conversation between many people. Answer option D is incorrect. A pull technique
describes the recipients of the report "pulling" the information, such as from a Website.
|
Question: 4
|
Your project team is executing
the project plan and things are going well. Your team has reached its first milestone and is now in the second phase of the project. The project stakeholders
have requested that you find a method to reduce the duration of the project. They will reward you and your project team with a 25 percent
bonus of the project costs if you can finish the project thirty days earlier than what was already planned. The stakeholders, however, will not
approve any additional labor costs as part of the agreement. Which approach could you use to shorten the duration of the project?
A. Perform resource leveling
for the project.
B. Crash the project schedule.
C. Fast track the project.
D. Remove things from the
project scope.
|
Answer: C
|
Explanation:
Fast tracking is a technique
for compressing project schedule. In fast tracking, phases are overlapped that would normally be done in
sequence. It is shortening the
project schedule without reducing the project scope. It does not add any additional labor but it can introduce project risks. Answer option D is incorrect. Removing things
from the project scope can reduce the project duration, but it will not satisfy the
requirements the stakeholders have
identified. Answer option A is
incorrect. Resource leveling can actually increase the project duration. Answer option B is incorrect. Crashing can
reduce the project duration but it increases the labor expense, something the stakeholders won't approve.
|
Question: 5
|
The Define Activities process
is the first process in the project time management knowledge are
a. The Define Activities
process creates just three outputs as a result of decomposition, rolling wave planning, templates, and expert judgment.
Which one of the following is not an output of the Define Activities process?
A. Activity list
B. Milestone list
C. Activity attributes
D. Project document updates
|
Answer: D
|
Explanation:
Project document updates are
not an output of the Define Activities process. Project document updates are the outputs for estimate activity
resources. Project document updates include the following: Activity list Activity attributes Resource calendars Answer option A is incorrect. The activity
list is an output of the define activities process. Answer option C is incorrect. The activity
attributes is an output of the define activities process. Answer option B is incorrect. The milestone
list is an output of the define activities process.
|
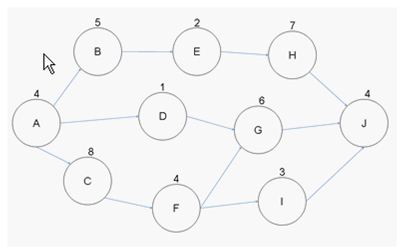
Question: 6
|
Examine the figure given
below:
If Activity B takes eight days
to complete instead of five days as schedule, how long can you now delay Activity H?
A. Three days
B. One day
C. Four days
D. Zero days
|
Answer: B
|
Explanation:
Activity B is not on the
critical path and it has a total of four days of float. If Activity B takes a
total of eight days, it will consume
three days of float. However, the total
duration of the path ABEHJ may not exceed 26 days, as this is the total duration for the project. Although Activity H has a total of four days of float available,
the consumption of three days of float on this path will reduce the total float for Activity H to just
one day. If Activity H is delayed by
more than one day, then the project will be late. Answer option D is incorrect. There is one day
of float still available for Activity H. Answer options A and C are incorrect. These
are not the valid answers, as there is just one day of float available for Activity H.
|
Question: 7
|
You are the project manager of
the GHT Project. Ben, one of your project team members, does not understand the idea of a milestone. Which of
the following best describes what a milestone is?
A. A significant point in the
project
B. A goal of reaching a
significant delivery of project benefits by an identified date
C. An imposed date for the
project to reach a given point
D. The completion of a project
activity that is crucial to project completion
|
Answer: A
|
Explanation:
A milestone is simply a
significant point or event in the project. It does not have to be assigned to a
specific date, but is usually assigned
to the completion of project phases. A milestone is the end of a stage that marks
the completion of a work package or phase, typically mark d by a high level event such as completion, endorsement or signing of a deliverable,
document or a high level review meeting. In addition to signaling the completion of a
key deliverable, a milestone may also signify an important decision or the derivation of a
critical piece of information, which
outlines or affects the future of a project. In this sense, a milestone not only signifies distance traveled (key stages in a project) but also indicates direction of
travel since key decisions made at milestones may alter the route through the project plan. To create a milestone, enter 0 (zero) in the
Duration field. The task will automatically be classified as a milestone. Answer option C is incorrect. This is a
project constraint. Answer option B is
incorrect. A project goal is an objective for time, cost, scope, and other metrics.
Answer option D is incorrect. All
activities must be completed in order to complete the project work. Activities that are not completed are quality issues that prevent the project from
completing the project scope.
|
Question: 8
|
You are the project manager of
the GHY Project. Management wants you to create a process improvement plan for
your project. Your project will be studied by management and will become a standard for all future organizational
projects based on your project's performance, approach, and implementation of project processes. All of
the following should be included in your project's process improvement plan except for which one?
A. Process boundaries
B. Process configuration
C. Targets for improved
performance
D. Identification of project
risks
|
Answer: D
|
Explanation:
Identification of the project
risks is not part of the process improvement plan. Identify risks is a risk management process, and risks are recorded in
the risk register. Answer options A, B,
and C are incorrect. Process boundaries, Process configuration and Targets for improved performance are parts of the process improvement plan.
|
Question: 9
|
George is the project manager
of the NHQ Project and has a budget of $778,000. The project is scheduled to last for one year with an equal
amount of work completed each quarter. The second quarter of the project has ended and George
has spent $325,000 but has only finished forty percent of the project. Management needs a variance
report for the project schedule. What value should George report in this instance?
A. .96
B. -$77,800
C. $-34,500
D. -$13,800
|
Answer: B
|
Explanation:
Schedule variance (SV) is a
measure of schedule performance on a project. The variance notifies that the schedule is ahead or behind what was planned for this period in time. The
schedule variance is calculated based on the following formula: SV = Earned Value (EV) - Planned Value (PV) If the resulting schedule is negative, it
indicates that the project is behind schedule. A value greater than 0 shows that the project is ahead of the planned schedule. A value of 0 indicates
that the project is right on target. The earned value in this instance is forty percent of the project budget, $778,000, and the planned value is
$398,000 because George is to be fifty percent done at the end of the second quarter, as the work is spread evenly across all quarters. The
schedule variance is -$77,800 for the project. Answer option A is incorrect. .96 represents
the cost performance index. Answer
option C is incorrect. -$34,500 represents the project's variance at completion
if the project continues as is. Answer option D is incorrect. -$13,800 is the cost variance for
the project.
|
Question: 10
|
You are the project manager of
the NHQ Project. Management has set a conformance to the project schedule for your project at 0.95. What does
this term mean?
A. It means the largest
schedule variance you can have is five percent.
B. It is the earned value
divided by the planned value for your project.
C. It is the expectation of
management to be 95 on schedule at 95 percent of the project.
D. It means you will need to
earn at least 95 cents per dollar invested in the project.
|
Answer: A
|
Explanation:
Conformance to schedule is a
required adherence for the project's schedule. In this instance, the project manager must not allow the schedule to
slip more than five percent. Answer
option B is incorrect. This is the description of the schedule performance
index. Answer option D is incorrect.
This is the description of the cost performance index. Answer option C is incorrect. This is not a
valid statement about the project performance.
|
Question: 11
|
Which one of the following
estimate types is a form of expert judgment?
A. Parametric estimate
B. Analogous estimate
C. Bottom-up estimate
D. Definitive estimate
|
Answer: B
|
Explanation:
An analogous estimate is a
form of expert judgment because it relies on historical information. The historical information, assuming that it is
accurate, serves as the conduit to the expert that created the historical information. Answer option C is
incorrect. A bottom-up estimate creates an activity duration estimate for each work package in the
WBS. Answer option A is incorrect. Parametric estimating uses a parameter, such as 10 hours
per fixture installation, as a base to predict the duration of the project. Answer option D is
incorrect. A definitive estimate, also known as a bottom- up estimate, accounts
for the cost of each work package.
|
Question: 12
|
You are the project manager of
the NHA Project. This project is expected to last one year with quarterly milestones throughout the year. Your
project is supposed to be at the third milestone today but you're likely only 60 percent
complete. Your project has a BAC of $745,000 and you've spent $440,000 of the budget-to-date. What is
your schedule performance index for this project?
A. 80
B. 1.02
C. 102
D. 0.80
|
Answer: D
|
Explanation:
The schedule performance index
can be found by dividing the earned value by the planned value. In this project, it's $447,000 divided by the
$558,750 for a value of 0.80. Schedule
performance index (SPI) is the measure of schedule efficiency on a project. It
is used in trend analysis to predict
future performance. SPI is the ratio of
earned value to planned value. The SPI is calculated based on the following formula:
SPI = Earned Value (EV) /
Planned Value (PV)
If the SPI value is greater
than 1, it indicates better than expected performance, whereas if the value is less than 1, it shows poor performance. The SPI value of 1 indicates that
the project is right on target.
Answer option A is incorrect.
"80" is not the same value as ".80". Answer option B is incorrect. 1.02 is the cost
performance index. Answer option C is
incorrect. 102 is not a valid calculation for this question.
|
Question: 13
|
Fill in the blank with an
appropriate phrase.
The __________ includes a
description of any collateral services required, such as performance reporting or post-project operational support for the procured item.
|
Answer:
|
procurement SOW Explanation: The procurement SOW consists of
a description of some collateral services required, such as performance reporting or post- project operational support for the procured
item. The procurement SOW is revised and refined as required when it moves through the procurement process until incorporated into a
signed contract award.
|
Question: 14
|
Mark is the project manager of
the GHQ Project. He is happily reporting that his project has a schedule performance index of 2.12. Management, however, does not think this is
good news. What is the most likely reason why management does not like an SPI of 2.12?
A. It is not good news because
a larger number means the schedule duration estimates were likely to be wrong to begin with.
B. They likely do not
understand the SPI formula.
C. It is not good news, as the
number should be closer to 100 than 0.
D. It is good news, but Mark
may have large cost variances to achieve this value.
|
Answer: A
|
Explanation:
Cost and schedule performance
indexes should be as close to 1 as possible. A larger value, such as 2.12, means that the schedule duration estimates were likely bloated or incorrect to
begin with. Answer option B is
incorrect. This is not the best choice for this question. Answer option C is incorrect. The number
should not be close to 100; it should be close to 1. Answer option D is incorrect. While Mark may
have crashed the schedule and driven up costs to achieve the SPI value, a more likely reason is
that the time estimates were bloated.
|
Question: 15
|
You are the project manager of
the BHG Project. You are creating a network diagram as shown in the figure:
Mary, a project team member,
reports that an identified risk is likely to happen in the project that will affect the completion date of Activity D
. She reports that the risk event will likely cause the duration of the activity to increase by six
days. If this happens what is the earliest the project can complete?
A. 32 days
B. 29 days
C. 27 days
D. 26 days
|
Answer: D
|
Explanation:
If Activity D increases by six
days, the duration of the project will not change. There is 11 days of float available for Activity D so it may delay
by six days without affecting the project end date. What is float? Float or total float (TF) is the total amount
of time that a schedule activity may be delayed from its early start date without delaying the project
finish date, or violating a schedule constraint. It is calculated by using the critical path method
technique and determining the difference between the early finish dates and late finish dates.
Answer options A, B, and C are incorrect. These are not valid answers for the question.
|
Question: 16
|
Sam is the project manager of
the NQQ project. He and the project team have completed the stakeholder identification process for his
project. What is the main output of the identify stakeholders process?
A. Communications management
plan
B. Stakeholder register
C. Requirements
D. Stakeholder management
strategy
|
Answer: B
|
Explanation: According to the
PMBOK, the main output of the identify stakeholders process is the stakeholder register. The stakeholder register
is a project management document that contains a list of the stakeholders associated with the
project. It assesses how they are
involved in the project and identifies what role they play in the organization.
The information in this document can be
very perceptive and is meant for limited
exchange only. It also contains relevant information about the stakeholders, such as their requirements, expectations, and influence on the project. Answer option A is incorrect. The
communications management plan is an output of communications planning. Answer option D is incorrect. The stakeholder
management strategy is an output of stakeholder identification, but it is not the main output.
Answer option C is incorrect.
Requirements are not an output of the stakeholder identification process.
|
Question: 17
|
You work as a project manager
for BlueWell Inc. Management has asked you not to communicate performance unless the CPI is less than 0.96 or the SPI dips below 0.98. What type of
report would you create for management, if these instances develop in your project?
A. Cost variance report
B. Exceptions report
C. Performance management
report
D. Schedule variance report
|
Answer: B
|
Explanation:
The best answer is simply an
exception report.
An exception report refers and
documents the major mistakes, mishaps, and goofs. In other words, it itemizes the important and critically significant piece of documentation that is
vital to the proper and effective functioning of a project. It does not document what has gone right, but rather documents what has gone wrong. Answer option C is incorrect. A performance
management report is not a valid project management report. Answer option A is incorrect. The question is
asked a out cost and schedule so this answer would not be appropriate for both the cost and the schedule. Answer option D is incorrect. The question is
asked about cost and schedule so this answer would not be appropriate for both the cost and the schedule.
|
Question: 18
|
You are the project manager of
the HQQ Project. Your project is running late by ten percent of where you should be at this time. Management
is concerned. Considering that the project has a BAC of $567,899, you are thirty percent complete,
and you have spent $179,450. What is this project's to-complete performance index based
on the current BAC?
A. 1.02
B. 0.010
C. 0.75
D. 0.95
|
Answer: A
|
Explanation: This project is
not performing well on schedule, but moderately well on costs. The project's TCPI based on the current BAC is
1.02. To-complete Performance Index (TCPI) is the measured projection of the anticipated
performance required to achieve either the BAC or the EAC. TCPI indicates the future required cost
efficiency needed to achieve a target EAC (Estimate At Complete).Once approved, the EAC supersedes
the BAC as the cost performance goal. Any significant difference between TCPI and the
CPI needed to meet the EAC should be accounted for by management in their forecast of the final
cost. The formula for TCPI is as
follows: TCPI = {(BAC-EV)/(BAC-AC)} Answer option D is incorrect. 0.95 is the
project's TCPI value based on the estimate at completion. Answer option C is incorrect. 0.75 is the
project's schedule performance index. Answer
option B is incorrect. 0.010 is not a valid calculation.
|
Question: 19
|
Andy works as the project
manager for Bluewell Inc. He is developing the schedule for the project. There are eight tools and techniques that a
project manager can use to develop the project schedule. Which of the following is a tool and
technique for the Schedule Development process?
A. Schedule compression
B. Reserve analysis
C. Variance analysis
D. Expert judgment
|
Answer: A
|
Explanation:
Schedule compression is a tool
used as part of the Schedule Development process. The tools and techniques for schedule
development are as follows: Schedule network
analysis Critical path method Critical chain method Resource leveling What-if scenario analysis Applying leads and lags Schedule compression Scheduling tool Answer options D, B, and C are incorrect.
These are not tools and techniques for schedule development.
|
Question: 20
|
You are the project manager
for your organization. You have recorded the following duration estimates for an activity in your project:
optimistic 20, most likely 45, pessimistic 90. What time will you record for this activity?
A. 48
B. 20o, 45m, 90p
C. 90
D. 45
|
Answer: A
|
Explanation:
This is an example of a
three-point estimate. A three-point estimate records the optimistic, most likely, and the pessimistic duration, and then
records an average for the predicted duration Three-point estimate is a way to enhance the
accuracy of activity duration estimates. This concept is originated with the Program Evaluation and
Review Technique (PERT). PERT charts the following three estimates:
Most likely (TM): The duration
of activity based on realistic factors such as resources assigned, interruptions, etc. Optimistic (TO): The activity duration based
on the best-case scenario Pessimistic
(TP): The activity duration based on the worst-case scenario The expected (TE) activity duration is a
weighted average of these three estimates: TE = (TO + 4TM + TP) / 6 Duration estimates based on the above
equations (sometimes simple average of the three estimates is also used) provide more accuracy. It can be calculated as follows: TE = ( 20 + 45*4 + 90) / 6 = 290/6 =48 Answer
options B, C, and D are incorrect. These are not the valid answers for this
question.
|
Question: 21
|
You are the project manager of
the NHQ Project. You have created the project network diagram as shown in the figure:
You are concerned about a risk
on Activity G that if it happens will delay the project by four days. You would like to utilize float for Activity G
. How much float is available for Activity G to help offset the risk event?
A. Five days
B. Four days
C. Eleven days
D. Zero
|
Answer: D
|
Explanation:
There is no float available
for Activity G because it is on the critical path. Float or total float (TF) is the total amount
of time that a schedule activity may be delayed from its early start date without delaying the project
finish date, or violating a schedule constraint. It is calculated by using the
critical path method technique and determining the difference between the early finish dates and late finish dates.
Answer options B, A, and C are incorrect. There is no float available for Activity G because it is on the
critical path.
|
Question: 22
|
Beth is the project manager
for her organization. Her current project has many deliverables that have been defined at a high level, but the
details of the deliverables are still unknown. In her project, Beth is planning in detail only the activities
that are most imminent in the project work. This approach to project management planning is
known as what?
A. Imminent activity
management
B. Rolling wave planning
C. Predecessor-only
diagramming
D. Decomposition
|
Answer: B
|
Explanation: Rolling wave
planning is a technique to plan and do the most imminent project work before moving onto the details that are far
off in the project schedule and project plan. Rolling wave planning is a technique for
performing progressive elaboration planning where the work to be accomplished in the near future is
planned in detail at a low level of the work breakdown structure. The work to be performed within
another one or two reporting periods in the near future is planned in detail as work is
being completed during the current period. Answer option D is incorrect. Decomposition is
the process of breaking down work packages into the activity list. Answer options A and C are incorrect. These
are not valid project management terms.
|
Question: 23
|
Gina is the project manager
for her organization and she is working with her project team to define the project activities. In this project, the
stakeholders are sensitive to the project completion date, so Gina is stressing to her project team
members that while they need to provide and account for all of the project activities, they should focus
on one work package in the WBS at a time. In order to start the decomposition of the project work
packages into activities, Gina will need all of the following except for which one?
A. Scope baseline
B. Organizational process
assets
C. WBS
D. Enterprise environmental
factors
|
Answer: C
|
Explanation: According to the
PMBOK, Gina will not need the WBS directly, but will rely on the scope baseline.A Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) in
project management is a tool that defines a project and groups the project's discrete work
elements in
a way that helps organize and
define the total work scope of the project. A WBS element may be a product, data, a service, or any combination. WBS also provides the necessary
framework for detailed cost estimating and control along with providing guidance for schedule development and control. Answer option A is incorrect. The scope
baseline is an input to define the project activities. Answer option D is incorrect. Enterprise
environmental factors are an input to define the project activities. Answer option B is incorrect.
Organizational process assets are an input to define the project activities.
|
Question: 24
|
You have created the project
network diagram for the ABC project. You are exploring total float and free float for that project. Martin, a project
team member, wants to know the difference between total float and free float. What is the
difference between total float and free float?
A. Total float is the amount
of time an activity can be delayed without delaying any project successors, whereas free float is the amount
of time an activity can be delayed without delaying the project completion date.
B. Total float is the amount
of time an activity can be delayed without delaying the project completion date, whereas free float is the
amount of time an activity can be delayed without delaying any project successors.
C. Total float is the amount
of time an activity can be delayed without delaying the project completion date, whereas free float is the
amount of time an activity can be delayed without delaying any project predecessors.
D. Total float is the amount
of time a non-critical activity can be delayed without delaying any project successors, whereas free float is the
amount of time an activity can be delayed without delaying the project completion date.
|
Answer: B
|
Explanation: Total float is
the time you can delay an activity without delaying the project end date, whereas free float is on each activity and
does not affect the early start date of successor activities. Float, also called slack, is the amount of
time an activity can be delayed without affecting any subsequent activities. There are two types of
floats available: Free Float: It is the
amount of time a schedule activity can be delayed without delaying the early start date of any immediately following schedule activities. Total Float: It is the total amount of time
that a schedule activity may be delayed from its early start date without delaying the project finish date, or violating schedule constraint.
Float is calculated by using the critical
path method technique. Answer options C,
A, and D are incorrect. These are not accurate definitions of free float and
total float.
|
Question: 25
|
John works as a project
manager of the NHQ Project. He has created the project network diagram as shown in the figure:
Based on the project network
diagram, how much float is available for Activity H if Activity B is delayed by four days and Activity E is delayed
by two days?
A. Zero
B. One
C. Four
D. Five
|
Answer: A
|
Explanation: The path of ABEHJ
will take 22 days to complete and cannot exceed 28 days or else the project will be late. If Activity B takes four
additional days and Activity E takes two
additional days, this adds (4+2= 6) six days to the path, bringing the path's duration to exactly (22+6 = 28) days. There is no available float left for
Activity D or H. Float or total float
(TF) is the total amount of time that a schedule activity may be delayed from
its early start date without delaying
the project fish date, or violating a
schedule constraint. It is calculated by using the critical path method technique and determining the difference between the early finish dates and
late finish dates. Answer options B, C,
and D are incorrect. There is no float available because the path's duration
has increased to 28 days.
|
Question: 26
|
Ben is the project manager for
his organization. His project has 26 stakeholders this week and will have five additional stakeholders next week.
How many more communication channels will Ben's project have next week?
A. 140
B. 10
C. 325
D. 5
|
Answer: A
|
Explanation:
Ben's project will have 140
more communication channels because of the five additional stakeholders. To solve the question, you will
need to find the current stakeholder
communication channels first, which is (26*25)/2= 325, and then find the difference of the number of channels for the five additional stakeholders. You can use the formula of N(N-1), where N is
the number of stakeholders. In this example, the formula would read: Total number of communication channels that
Ben will have next = ((31*30)/2)-((26*25)/2 =140 Answer
option D is incorrect. Five is the number of additional stakeholders. Answer option B is incorrect. 10 is the number
of communication channels among just five stakeholders. Answer option C is incorrect. 325 is the
number of current communication channels.
|
Question: 27
|
You are the project manager
for your company. You are working with the activities defined in the figure below.
What will happen to your
project if Activity F takes five additional days to complete than what was expected?
A. Your project's critical
path will shift to ACFI.
B. Your project will be late
by five days.
C. Your project can still
complete on time as float is available on Activity I.
D. Your project will now have
two critical paths.
|
Answer: B
|
Explanation: Activity F is on
the critical path of ACFHK of 30 days. By adding five additional days to Activity F, the project will now take 35 days
to complete. Answer options C, A, and D are incorrect. These are not the valid answers.
|
Question: 28
|
You are the project manager
for your organization. You need the oak cabinets for your project delivered by December 1 in order to install
the floors around the oak cabinets by December 15. Your company's procurement office generally takes
45 days to complete procurement orders. Based on this information, how should
you schedule the lead time for the cabinet delivery?
A. Cabinet procurement
December 1, plus 45 days lead time
B. Cabinet procurement
November 15
C. Cabinet procurement
December 1, minus 45 days lead time
D. Cabinet procurement
December 15 minus 45 days lead time
|
Answer: C
|
Explanation:
The cabinet procurement and
delivery must be completed by December 1. By scheduling the activity to finish on December 1 with minus 45 days lead time for procurement, the cabinets
will arrive by the needed date. Answer
option A is incorrect. Lead time is always negative time, lag time is positive
time. This choice would cause the
cabinets to not arrive until 45 days
after December 1. Answer option D is
incorrect. This choice would cause the cabinets to arrive on December 15 when the floors are to be installed. Answer option B is incorrect. This choice is
not the best answer because it does not necessarily account for holidays, weekends, or other factors in the project calendar. By scheduling
the cabinet for December 1 and working backwards through lead time, the project's PMIS will account for these breaks in the project work.
|
Question: 29
|
Your project has a BAC of
$750,000 and is 75 percent complete. According to your plan, however, your project should actually be 80 percent
complete. You have spent $575,000 of your project budget to reach this point and you are worried
about the project not being able to complete based on your current project budget. What is the
to-complete performance index for this project?
A. 0.98
B. -$16,677
C. 1.07
D. 0.94
|
Answer: C
|
Explanation:
The to-complete performance
index can be found by using the formula (BAC-EV)/(BAC-AC) for a value of 1.07. The higher the value is from 1,
the less likely the project will meet the BAC. To-complete Performance Index (TCPI) is the
measured projection of the anticipated performance required to achieve either the BAC or the EAC. TCPI indicates the future required cost
efficiency needed to achieve a target EAC (Estimate At Complete).Once approved, the EAC supersedes the BAC as the cost performance
goal. Any significant difference between TCPI and the CPI needed to meet the EAC should be accounted for by management in their forecast
of the final cost. The formula for TCPI
is as follows: TCPI =
{(BAC-EV)/(BAC-AC)} Answer option A is
incorrect. 0.98 is the project's cost performance index. Answer option D is incorrect. This is the
project's schedule performance index. Answer
option B is incorrect. -$16,667 is the project's variance at completion.
|
Question: 30
|
You are the project manager of
the NHT Project. This project has 12,345 office doors to install throughout a campus. Each of the doors costs
the project $456 and requires special hardware to electronically lock and open the doors. You've
gathered the project team before they begin the installation for a hands-on training. As a
group you and the project team install 50 doors following a checklist of instructions so that
every door will be installed exactly the same throughout the campus and with minimal waste. This is an
example of what project execution technique?
A. Preventive action
B. Defect repair validation
C. Implemented corrective
action
D. Quality control
|
Answer: A
|
Explanation: This is an
example of a preventive action as you're working with the team before they install the doors to train them on the
installation. The checklist is a quality control tool but the question was asking for a project execution
activity. Preventive and corrective actions are part of project execution. Answer option D is incorrect. Quality control
is a controlling and monitoring process, not an executing process. Answer option B is incorrect. The defect
repair validation comes after the project team has corrected an error - something that has not occurred in this instance. Answer option C is incorrect. Corrective
action is a response to something that needs to be corrected in the project.






No comments:
Post a Comment